Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new medication or weight management program.
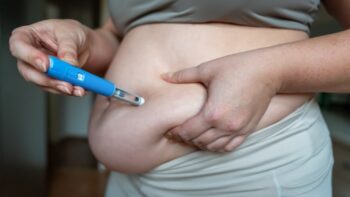
GLP‑1 receptor agonists, such as Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro, have gained attention for their ability to support weight management and improve blood sugar control. While these medications can be effective tools, they are not suitable for everyone. Understanding who may benefit — and who should proceed with caution — is key to making safe and informed decisions.
What Are GLP‑1 Medications?
GLP‑1, or glucagon-like peptide-1, is a naturally occurring hormone that helps regulate blood sugar, slows digestion, and promotes a feeling of fullness. Medications that mimic this hormone can help people reduce appetite, control portions, and manage blood glucose levels.
GLP‑1 medications were initially developed for type 2 diabetes but are now widely prescribed for weight management in individuals with obesity or overweight who have weight-related health conditions. They are usually administered as a weekly injection under a doctor’s supervision.
Who Might Be a Candidate?
GLP‑1 medications are not a first-line treatment for weight loss. Healthcare providers typically consider them for individuals who meet certain criteria, including:
- Adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, classified as obese.
- Adults with a BMI of 27 or higher who also have weight-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol.
- Individuals who have struggled to achieve weight loss through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes alone.
It’s important to note that GLP‑1 medications are most effective when combined with healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity. They are not a replacement for long-term behavior changes.
Potential Benefits
People who use GLP‑1 medications for weight management may experience several benefits:
- Appetite Control: GLP‑1 slows gastric emptying, which helps reduce hunger and cravings.
- Steady Weight Loss: Many users report gradual, sustained weight loss when combined with lifestyle changes.
- Improved Blood Sugar Management: For individuals with type 2 diabetes, GLP‑1 medications can help stabilize blood glucose levels.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Some research suggests potential heart health benefits, including reduced risk factors associated with obesity and diabetes.
These benefits make GLP‑1 medications an attractive option for people who have not achieved significant results through diet and exercise alone.
Who Should Be Cautious
GLP‑1 medications are not suitable for everyone. Certain individuals should avoid these drugs or use them only under close supervision:
- People with a history of medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2).
- Individuals with a history of pancreatitis, as GLP‑1 medications can increase the risk of pancreatic issues.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, unless specifically advised by a healthcare provider.
- Anyone with serious gastrointestinal disorders that could be worsened by delayed stomach emptying.
A thorough medical evaluation is essential before starting a GLP‑1 medication to ensure safety and suitability.
Side Effects to Know
Most side effects are mild to moderate, but users should be aware of what to expect. Common side effects include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal discomfort or bloating
- Temporary appetite changes
Side effects often improve over time as the body adjusts. Rare but serious complications, such as pancreatitis or gallbladder issues, require immediate medical attention. Monitoring by a healthcare provider is critical to manage risks.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
GLP‑1 medications are most effective when paired with healthy lifestyle changes. Medication alone is unlikely to produce optimal results. Key strategies include:
- Balanced Diet: Emphasize whole foods, vegetables, lean proteins, and controlled portions.
- Regular Physical Activity: Incorporate cardiovascular and strength exercises to support metabolism and overall health.
- Behavioral Strategies: Track food intake, practice mindful eating, and address emotional eating patterns.
Combining medication with sustainable lifestyle habits increases the likelihood of long-term success.
Questions to Discuss With Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting GLP‑1 therapy, it’s important to have a detailed conversation with your healthcare provider. Key questions might include:
- Am I a good candidate for this medication based on my BMI and health history?
- What is the expected timeline and degree of weight loss?
- What side effects should I anticipate, and how can they be managed?
- How will this medication interact with any current prescriptions?
- What lifestyle changes should I commit to while on the medication?
Open communication ensures that the treatment plan is tailored to your needs and maximizes both safety and effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
GLP‑1 medications, including Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro, can be effective tools for weight management and blood sugar control for the right individuals. They are not a magic solution but work best in combination with healthy lifestyle habits.
Candidates typically include adults with obesity or overweight who have related health conditions and who have struggled with traditional weight-loss strategies. Careful screening, ongoing monitoring, and realistic expectations are essential for safe and effective use.
By understanding whether GLP‑1 medications are appropriate for your situation and discussing them with a healthcare professional, you can make informed decisions that support long-term health and well-being.
By Admin –